Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems. The very name can evoke a mix of excitement and apprehension. For businesses hitting a growth plateau, or struggling to manage disparate systems, ERP promises streamlined processes, improved visibility, and ultimately, a more efficient and profitable operation. But the landscape of ERP solutions is vast and often confusing, with varying costs, functionalities, and deployment models. Among these options, open source ERP software stands out as a compelling alternative, offering flexibility, customization, and potentially lower upfront costs.
Having been involved in several ERP implementations, both proprietary and open source, I’ve seen firsthand the transformative impact a well-chosen and properly implemented system can have. I’ve also witnessed the potential pitfalls of choosing the wrong solution or failing to adequately plan for the transition. The key takeaway? ERP is not just about software; it’s about aligning technology with your business strategy. And open source ERP, with its inherent adaptability, can be a powerful tool in achieving that alignment.
This guide aims to provide a comprehensive overview of open source ERP software, exploring its features, benefits, challenges, and offering practical advice for businesses considering this path. We’ll delve into the core functionalities of ERP systems, compare open source options with proprietary solutions, and discuss the critical factors to consider when selecting and implementing an open source ERP. Whether you’re a small business owner or a seasoned IT professional, this article will equip you with the knowledge you need to make an informed decision about open source ERP.
What is Open Source ERP Software?
At its core, open source ERP software is an ERP system whose source code is freely available for anyone to use, modify, and distribute. This contrasts with proprietary ERP software, where the vendor retains exclusive control over the code and licenses it to users. The “open source” designation doesn’t necessarily mean the software is free of charge, although many open source ERP systems are available under a freemium model or with a community edition that is free to use. The real power lies in the ability to customize the software to precisely match your business requirements, something that’s often difficult or impossible with proprietary solutions.
Key Characteristics of Open Source ERP
Several key characteristics distinguish open source ERP software from its proprietary counterparts:
- Open Source License: The software is distributed under an open source license, such as the GNU General Public License (GPL) or the Apache License 2.0. These licenses grant users the freedom to use, study, modify, and distribute the software.
- Community-Driven Development: Open source ERP systems are often developed and maintained by a community of developers, users, and contributors. This collaborative approach can lead to faster innovation and more robust solutions.
- Customizability: The availability of the source code allows businesses to customize the ERP system to meet their specific needs. This can involve adding new features, modifying existing workflows, or integrating with other systems.
- Flexibility: Open source ERP systems offer greater flexibility in terms of deployment options. They can be deployed on-premises, in the cloud, or in a hybrid environment.
- Transparency: The open nature of the code allows users to inspect it for security vulnerabilities and ensure that it meets their requirements.
Core Modules of an ERP System
Regardless of whether it’s open source or proprietary, an ERP system typically comprises several core modules that integrate to manage various aspects of a business. Understanding these modules is crucial for assessing the suitability of an ERP solution for your organization.
Common ERP Modules
- Financial Management: This module handles accounting, budgeting, financial reporting, and accounts payable/receivable. It’s the backbone of any ERP system.
- Supply Chain Management (SCM): SCM manages the flow of goods and services from suppliers to customers, including procurement, inventory management, warehousing, and logistics.
- Manufacturing: This module supports production planning, scheduling, shop floor control, and quality management. It’s essential for manufacturing companies.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): CRM focuses on managing customer interactions, sales, marketing, and customer service. It helps businesses build stronger customer relationships.
- Human Resources (HR): HR manages employee data, payroll, benefits, and recruitment. It streamlines HR processes and ensures compliance with labor laws.
- Project Management: This module helps plan, execute, and track projects, managing resources, timelines, and budgets.
- Inventory Management: Monitors and controls the stock levels of goods and materials. This module helps in preventing stockouts and reducing holding costs.
Benefits of Open Source ERP Software
Choosing an open source ERP system offers several potential advantages over proprietary solutions:
Cost Savings
While not always free, open source ERP systems often have lower upfront licensing costs compared to proprietary software. This can be a significant advantage for small and medium-sized businesses with limited budgets. However, remember to factor in the costs of implementation, customization, and ongoing maintenance.
Customization and Flexibility
The ability to customize the source code to meet specific business requirements is a major advantage of open source ERP. This allows businesses to tailor the system to their unique processes and workflows, something that’s often difficult or impossible with proprietary solutions. This flexibility also allows for integration with existing systems.
Community Support
Open source ERP systems often have active communities of developers and users who provide support, documentation, and contribute to the ongoing development of the software. This can be a valuable resource for businesses that need help with implementation, customization, or troubleshooting.
No Vendor Lock-In
With open source ERP, you’re not locked into a specific vendor. You have the freedom to choose your own implementation partner, hosting provider, and support team. This gives you greater control over your ERP system and avoids the potential for vendor lock-in.
Innovation and Agility
The community-driven development model of open source ERP can lead to faster innovation and more agile development cycles. New features and updates are often released more frequently than with proprietary software.
Challenges of Open Source ERP Software
While open source ERP offers many benefits, it also presents some challenges that businesses need to be aware of:
Implementation Complexity
Implementing an open source ERP system can be more complex than implementing a proprietary solution, especially if extensive customization is required. It often requires technical expertise and a thorough understanding of the business processes.
Lack of Dedicated Support
While community support is available, it may not be as comprehensive or responsive as the dedicated support offered by proprietary ERP vendors. Businesses may need to rely on their own IT staff or hire external consultants for support.
Security Concerns
While the open nature of the code allows for greater scrutiny, it also means that security vulnerabilities are potentially more exposed. Businesses need to ensure that they have adequate security measures in place to protect their data.
Ongoing Maintenance and Updates
Maintaining and updating an open source ERP system requires ongoing effort and expertise. Businesses need to ensure that they have the resources to keep the system secure, stable, and up-to-date.

Hidden Costs
While the initial licensing costs may be lower, the total cost of ownership of an open source ERP system can be higher than expected due to implementation, customization, support, and maintenance costs. It’s crucial to carefully estimate these costs before making a decision.
Choosing the Right Open Source ERP Software
Selecting the right open source ERP system for your business is a critical decision. Here are some factors to consider:
Assess Your Business Needs
Start by thoroughly assessing your business needs and requirements. Identify the key processes that you want to streamline, the functionalities that you need, and the integrations that are required. Create a detailed list of requirements and prioritize them based on their importance.
Evaluate Different Options
Research different open source ERP systems and evaluate their features, functionality, and suitability for your business. Consider factors such as the size of the community, the availability of documentation, and the reputation of the vendor or community. Popular options include Odoo, ERPNext, and Apache OFBiz.
Consider Scalability
Ensure that the ERP system can scale to meet your future needs as your business grows. Consider factors such as the number of users, the volume of transactions, and the complexity of your business processes.
Check for Integrations
Verify that the ERP system can integrate with your existing systems, such as CRM, e-commerce platforms, and other business applications. Seamless integration is essential for ensuring data consistency and avoiding data silos.
Look for Customization Options
Assess the customization options offered by the ERP system. Determine whether you can easily customize the system to meet your specific needs or whether you will need to hire external consultants for customization.
Consider the Total Cost of Ownership
Estimate the total cost of ownership of the ERP system, including implementation, customization, support, maintenance, and training costs. Compare the total cost of ownership of different options before making a decision.
Test the Software
Before making a final decision, test the ERP system thoroughly to ensure that it meets your requirements and that it is easy to use. Consider conducting a pilot project to test the system in a real-world environment.
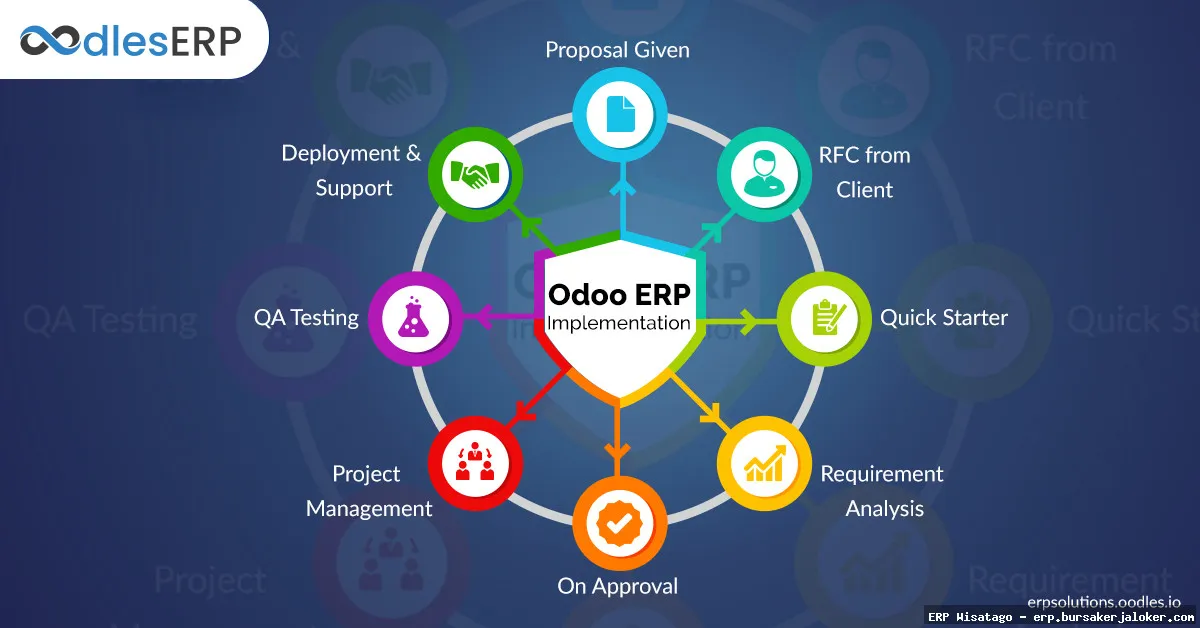
Implementation Best Practices
Implementing an open source ERP system successfully requires careful planning and execution. Here are some best practices to follow:
Plan Thoroughly
Develop a detailed implementation plan that outlines the scope of the project, the timeline, the resources required, and the responsibilities of each team member. A well-defined plan is essential for ensuring a smooth and successful implementation.
Involve Key Stakeholders
Involve key stakeholders from all departments in the implementation process. This will help ensure that the ERP system meets the needs of all users and that everyone is on board with the changes.
Provide Adequate Training
Provide adequate training to all users on how to use the ERP system. This will help ensure that they can effectively use the system and that they are comfortable with the new processes.
Data Migration
Plan and execute the data migration process carefully. Ensure that all data is accurately migrated to the new ERP system and that there is no data loss or corruption.
Testing and Validation
Thoroughly test and validate the ERP system after implementation to ensure that it is working correctly and that it meets all requirements. Conduct user acceptance testing to ensure that the users are satisfied with the system.

Ongoing Support and Maintenance
Provide ongoing support and maintenance to ensure that the ERP system remains stable, secure, and up-to-date. This includes monitoring the system for performance issues, applying security patches, and providing user support. Effective IT management often requires a robust system, with RMM playing a crucial role in monitoring and maintaining infrastructure
.
Conclusion
Open source ERP software offers a compelling alternative to proprietary solutions, providing flexibility, customizability, and potentially lower costs. However, it also presents challenges such as implementation complexity and the need for technical expertise. By carefully assessing your business needs, evaluating different options, and following implementation best practices, you can successfully implement an open source ERP system that streamlines your processes, improves visibility, and helps you achieve your business goals. Remember that ERP is a journey, not a destination. Continuous improvement and adaptation are key to maximizing the value of your ERP investment.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about open source ERP software
What are the biggest advantages of using open source ERP software compared to proprietary solutions, especially for small to medium-sized businesses (SMBs)?
Open source ERP software offers several significant advantages for SMBs compared to proprietary solutions. The most notable is often the lower upfront cost, as there are typically no licensing fees. This can be a substantial saving, allowing businesses to allocate resources to other critical areas. Beyond cost, open source ERP systems offer greater flexibility and customization. Businesses can tailor the software to their specific needs without being locked into a vendor’s pre-defined features. This adaptability is crucial for growing companies. Furthermore, the open source community provides a vast network of support, including forums, documentation, and third-party developers. This collaborative environment fosters innovation and ensures ongoing maintenance and updates, often at a faster pace than proprietary software.
How secure is open source ERP software, and what steps should I take to ensure data protection and prevent security vulnerabilities?
The security of open source ERP is a common concern, but it’s important to understand that its security depends largely on how it’s implemented and maintained. While the open nature of the code allows for public scrutiny and quicker identification of vulnerabilities, it also means that malicious actors can potentially find and exploit those vulnerabilities. To ensure data protection, implementing a robust security strategy is crucial. This includes regular security audits, timely patching of known vulnerabilities, strong access controls, and employee training on security best practices. Using a web application firewall (WAF) can protect against common web exploits. Furthermore, encrypting sensitive data at rest and in transit, and regularly backing up data are essential steps. Choosing a reputable open source ERP vendor or provider with a strong security track record is also paramount. Ultimately, a proactive approach to security is key to mitigating risks associated with any ERP system, open source or proprietary.
What is the typical implementation process for an open source ERP system, and what kind of resources (time, personnel, budget) should a company expect to dedicate to a successful implementation?
Implementing an open source ERP system typically involves several stages: planning, installation, configuration, data migration, customization (if needed), testing, training, and go-live. The implementation process can be complex and time-consuming, so careful planning is essential. The resources required vary depending on the size and complexity of the business. Expect to dedicate significant time from key personnel, including IT staff, department managers, and end-users. A dedicated project manager is highly recommended. The budget should include costs for hardware, software (if any commercial modules are required), implementation services (if outsourced), training, and ongoing maintenance. Data migration is often a major effort, requiring careful planning and execution. Customization can significantly increase the time and cost of implementation. A phased rollout is often recommended to minimize disruption and allow for iterative improvements. Thorough testing and user training are crucial for a successful go-live.
