The construction industry, with its intricate project lifecycles, demanding regulations, and razor-thin margins, often feels like navigating a minefield. Juggling multiple projects, managing subcontractors, tracking materials, and staying compliant can quickly become overwhelming. For years, many construction companies relied on a patchwork of spreadsheets, disparate software solutions, and sheer grit to keep things afloat. But in today’s competitive landscape, this approach is simply unsustainable. That’s where Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems come in, offering a centralized, integrated solution to streamline operations and drive efficiency.
Think of an ERP system as the central nervous system of your construction business. It connects all your vital functions – from project management and accounting to procurement and human resources – into a single, unified platform. This integration eliminates data silos, improves communication, and provides real-time visibility into every aspect of your operations. Implementing an ERP is a significant undertaking, but the potential rewards – increased profitability, improved project delivery, and enhanced decision-making – are well worth the effort.
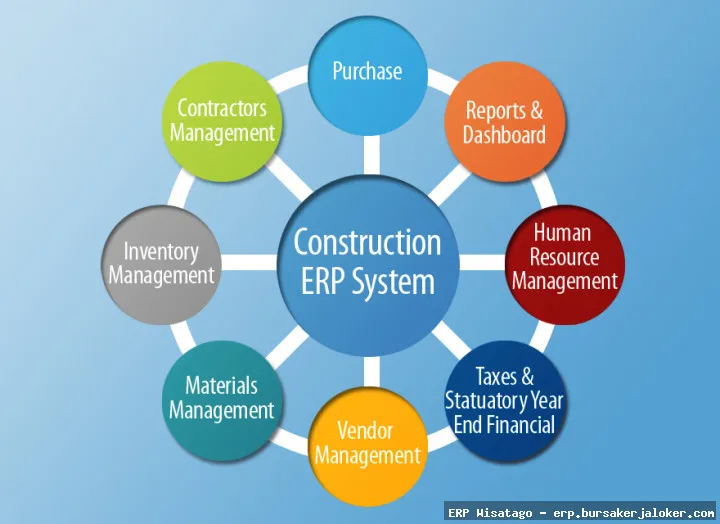
This comprehensive guide will delve into the world of ERP for the construction industry, exploring its key features, benefits, challenges, and best practices for successful implementation. We’ll examine how ERP can address the specific pain points faced by construction companies, from managing complex projects and tracking costs to ensuring compliance and optimizing resource allocation. Whether you’re a small contractor or a large construction firm, this guide will provide you with the knowledge and insights you need to determine if ERP is the right solution for your business and, if so, how to choose and implement the system that best meets your needs.
What is ERP for the Construction Industry?
ERP for the construction industry is a software suite designed to manage and integrate all aspects of a construction business, from project initiation to completion. Unlike generic ERP systems, construction ERPs are tailored to address the unique challenges and complexities of the construction process. This includes managing project costs, scheduling, resource allocation, equipment maintenance, and compliance with industry regulations. It’s about having a single source of truth for all your business data.
Key Differences Between Generic and Construction-Specific ERP
While generic ERP systems offer broad functionality across various business functions, construction-specific ERP systems provide specialized modules and features tailored to the industry. For example, a construction ERP will typically include features for:
- Job Costing: Detailed tracking of costs associated with individual projects, including labor, materials, and subcontractors.
- Project Management: Tools for planning, scheduling, and monitoring project progress.
- Equipment Management: Tracking equipment usage, maintenance schedules, and costs.
- Subcontractor Management: Managing subcontractor agreements, payments, and compliance.
- Change Order Management: Streamlining the process of managing and approving change orders.
Generic ERP systems may lack these specific functionalities, requiring construction companies to rely on separate, often disconnected, software solutions.
Benefits of Implementing ERP in Construction
Implementing an ERP system can bring a multitude of benefits to construction companies, leading to increased efficiency, reduced costs, and improved profitability.
Improved Project Management
ERP systems provide project managers with real-time visibility into project progress, costs, and resources. This allows them to identify potential issues early on and take corrective action before they impact the project timeline or budget. Features like Gantt charts, critical path analysis, and resource scheduling enable project managers to effectively plan and execute projects.
Enhanced Cost Control
One of the biggest challenges in construction is managing project costs. ERP systems provide detailed job costing capabilities, allowing companies to track all expenses associated with a project, including labor, materials, subcontractors, and equipment. This granular level of cost tracking enables companies to identify areas where they can reduce costs and improve profitability. Real-time cost tracking also allows for proactive budget adjustments, minimizing cost overruns. Effective IT management often involves understanding the tools used, where RMM plays a crucial role in streamlining operations
.
Streamlined Procurement and Inventory Management
ERP systems can automate the procurement process, from creating purchase orders to receiving and paying invoices. This reduces the risk of errors and ensures that materials are ordered and delivered on time. Inventory management features help companies track material levels, prevent stockouts, and optimize inventory levels.
Better Resource Allocation
Efficiently allocating resources – including labor, equipment, and materials – is crucial for successful project execution. ERP systems provide tools for resource scheduling and tracking, allowing companies to optimize resource utilization and minimize downtime. By understanding where resources are being used and how efficiently they are being used, construction companies can make data-driven decisions about resource allocation.
Improved Communication and Collaboration
ERP systems facilitate communication and collaboration between different departments and stakeholders involved in a project. By centralizing all project information in a single platform, ERP systems ensure that everyone is on the same page and has access to the latest information. This reduces the risk of misunderstandings and delays.
Enhanced Reporting and Analytics
ERP systems provide powerful reporting and analytics capabilities, allowing companies to track key performance indicators (KPIs) and gain insights into their operations. This data can be used to identify areas for improvement, make better decisions, and track progress towards business goals. From project profitability reports to resource utilization dashboards, ERP provides the data needed to make informed decisions.
Compliance and Risk Management
The construction industry is heavily regulated, and companies must comply with a variety of regulations related to safety, labor, and environmental protection. ERP systems can help companies manage compliance by tracking relevant data, generating reports, and automating processes. This reduces the risk of fines and penalties and ensures that companies are operating in a safe and responsible manner.
Key Features of Construction ERP Systems
A robust construction ERP system should include a range of features designed to address the specific needs of the industry.
Project Management Module
This module should include features for project planning, scheduling, budgeting, and tracking. It should allow project managers to create detailed project plans, assign tasks to resources, track progress against the plan, and identify potential issues early on.
Job Costing Module
This module should provide detailed tracking of all costs associated with a project, including labor, materials, subcontractors, and equipment. It should allow companies to compare actual costs against budgeted costs and identify areas where they can reduce costs.
Accounting and Financial Management Module
This module should handle all aspects of financial management, including general ledger, accounts payable, accounts receivable, and payroll. It should integrate with other modules in the ERP system to provide a complete view of the company’s financial performance.
Inventory Management Module
This module should track material levels, prevent stockouts, and optimize inventory levels. It should allow companies to track material usage, manage inventory locations, and generate reports on inventory levels.
Equipment Management Module
This module should track equipment usage, maintenance schedules, and costs. It should allow companies to schedule maintenance, track equipment downtime, and generate reports on equipment utilization.
Subcontractor Management Module
This module should manage subcontractor agreements, payments, and compliance. It should allow companies to track subcontractor performance, manage insurance certificates, and generate reports on subcontractor costs.
Document Management Module
This module should store and manage all project-related documents, including contracts, drawings, permits, and invoices. It should allow users to easily access and share documents, ensuring that everyone has access to the latest information.

Mobile Capabilities
In today’s mobile world, it’s essential that construction ERP systems offer mobile capabilities. This allows field workers to access and update project information from their mobile devices, improving communication and collaboration. Mobile features can include time tracking, expense reporting, and access to project documents.
Challenges of Implementing ERP in Construction
Implementing an ERP system is a complex undertaking, and construction companies should be aware of the potential challenges.
High Implementation Costs
ERP systems can be expensive to implement, especially for small and medium-sized businesses. Costs include software licenses, implementation services, training, and ongoing maintenance.
Resistance to Change
Implementing an ERP system requires significant changes to business processes, and employees may resist these changes. It’s important to communicate the benefits of the ERP system and provide adequate training to employees to ensure a smooth transition.
Data Migration
Migrating data from legacy systems to the new ERP system can be a complex and time-consuming process. It’s important to plan the data migration carefully and ensure that the data is accurate and complete.
Integration with Existing Systems
Construction companies often have a variety of existing software systems, such as accounting software, project management software, and estimating software. It’s important to ensure that the ERP system can integrate with these existing systems to avoid data silos.
Training and Support
Proper training and support are essential for successful ERP implementation. Employees need to be trained on how to use the ERP system effectively, and ongoing support should be available to address any issues that arise.
Choosing the Right ERP System for Your Construction Business
Selecting the right ERP system is a critical decision that can significantly impact the success of your implementation. Here are some key factors to consider.
Assess Your Business Needs
Before you start evaluating ERP systems, take the time to assess your business needs. Identify your pain points, define your goals for the ERP system, and determine which features are most important to you. Involve key stakeholders from different departments in this process to ensure that all needs are considered.
Evaluate Different ERP Vendors
Research and evaluate different ERP vendors to find a system that meets your specific needs. Consider factors such as the vendor’s experience in the construction industry, the system’s functionality, the cost of implementation, and the level of support provided. Request demos from multiple vendors to see the systems in action.
Consider Cloud-Based vs. On-Premise ERP
Decide whether you want a cloud-based or on-premise ERP system. Cloud-based ERP systems are hosted by the vendor and accessed over the internet, while on-premise ERP systems are installed on your own servers. Cloud-based systems typically have lower upfront costs and require less IT infrastructure, while on-premise systems offer more control over data and security.
Check References and Reviews
Talk to other construction companies that have implemented the ERP system you are considering. Ask them about their experience with the system, the vendor, and the implementation process. Read online reviews to get a broader perspective on the system’s strengths and weaknesses.
Negotiate a Contract
Once you have chosen an ERP system, negotiate a contract with the vendor. Make sure the contract clearly defines the scope of the implementation, the payment terms, the service level agreements, and the warranty terms.
Best Practices for Successful ERP Implementation
Following these best practices can help ensure a successful ERP implementation.
Get Executive Buy-In
Executive buy-in is essential for successful ERP implementation. Make sure that senior management is fully committed to the project and actively involved in the implementation process.
Establish a Project Team
Create a project team with representatives from different departments to oversee the implementation. The project team should be responsible for planning, executing, and monitoring the implementation process.
Develop a Detailed Implementation Plan
Create a detailed implementation plan that outlines the scope of the project, the timeline, the resources required, and the responsibilities of each team member. The implementation plan should be realistic and achievable.
Provide Adequate Training
Provide adequate training to employees on how to use the ERP system effectively. Training should be tailored to the specific roles and responsibilities of each employee.
Test the System Thoroughly
Test the ERP system thoroughly before going live. This includes testing all modules, integrations, and reports. Identify and fix any issues before the system is rolled out to the entire company.
Go Live in Phases
Consider going live in phases, rather than all at once. This allows you to identify and address any issues before they impact the entire company. Start with a pilot project or a small group of users, and then gradually roll out the system to the rest of the company.
Monitor and Evaluate Performance
After the ERP system is implemented, monitor and evaluate its performance. Track key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the success of the implementation and identify areas for improvement.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about ERP for construction industry
What are the key benefits of implementing an ERP system specifically designed for the construction industry, and how does it improve project management?
Implementing an ERP system tailored for the construction industry offers several significant advantages. Primarily, it provides centralized data management, integrating all project-related information, from budgeting and scheduling to resource allocation and procurement, into a single platform. This enhanced visibility allows for better project control, enabling project managers to track progress in real-time, identify potential bottlenecks, and make informed decisions. Furthermore, ERP systems facilitate improved cost control through accurate budgeting and expense tracking, minimizing cost overruns. Streamlined communication and collaboration among different departments and stakeholders also contribute to enhanced project efficiency and reduced errors. Ultimately, a construction ERP system boosts profitability by optimizing resource utilization and improving overall project outcomes.
How much does it typically cost to implement a construction ERP system, and what are the factors that influence the total cost of ownership (TCO)?
The cost of implementing a construction ERP system varies significantly based on several factors. Initial costs typically include software licensing fees, which can range from a few thousand to hundreds of thousands of dollars depending on the vendor and the number of users. Implementation costs, including system configuration, data migration, and user training, can also be substantial, often exceeding the software license fees. The total cost of ownership (TCO) is influenced by factors such as the size and complexity of the construction business, the number of users, the chosen deployment model (on-premise vs. cloud-based), and the level of customization required. Ongoing costs include maintenance, support, and potential upgrades. A thorough cost-benefit analysis, considering both direct and indirect benefits, is crucial before investing in a construction ERP system.
What are the essential features and modules that a construction-specific ERP system should have to effectively manage projects, finances, and resources?
A construction-specific ERP system should include several core features and modules to effectively manage projects, finances, and resources. Project management functionalities are crucial, encompassing scheduling, budgeting, resource allocation, and progress tracking. Financial management modules should handle accounting, job costing, billing, and payroll. Resource management capabilities are essential for tracking equipment, materials, and labor. Procurement management features should streamline the purchasing process, from vendor selection to order placement and invoice processing. Furthermore, document management functionality allows for centralized storage and organization of project documents. Integration with other systems, such as BIM (Building Information Modeling) and CRM (Customer Relationship Management), can further enhance the system’s capabilities. A robust reporting and analytics module is also vital for gaining insights into project performance and making data-driven decisions.
